Update() function returns “True” in any case the Insert/update attempt is successful on the supplied column, the significance of this function is to trigger the action/code only if the supplied column is get updated or inserted successfully.
In the below example, I’ve used the Update() function for identifying any changes in “CodeValue” column of table “Configtbl” and ignored the column changes if its value is same.
“Configtbl_Audit” table will get loaded based on the changes in “CodeValue” column in “Configtbl”
drop table if exists Configtbl
drop table if exists Configtbl_Audit
create table Configtbl(
Code nvarchar(10) not null,
CodeValue decimal(10,2) not null
)
insert into Configtbl(Code,CodeValue) values ('VA1111',25.99),('VA1118',19.99)
create table Configtbl_Audit(
Code nvarchar(10) not null,
Old_Value decimal(10,2) not null,
New_Value decimal(10,2) not null,
DateModified datetime not null
)
IF EXISTS (SELECT name FROM sys.objects WHERE name = 'TRG_UPD_NEW_OLD_VALUE' AND type = 'TR')
DROP TRIGGER TRG_UPD_NEW_OLD_VALUE
GO
CREATE TRIGGER TRG_UPD_NEW_OLD_VALUE
ON Configtbl
FOR UPDATE
AS
declare @oldvalue decimal(10,2),@newvalue decimal(10,2), @Code nvarchar(10)
IF (UPDATE (CodeValue))
BEGIN
select @oldvalue = CodeValue , @Code = Code from deleted
insert into Configtbl_Audit(Code, Old_Value, New_Value, DateModified)
select @Code, @oldvalue, CodeValue, getdate()
from inserted
where code=@Code
and @oldvalue <> CodeValue
END;
GO
Output:-
View of Data in Configtbl and Configtbl_Audit tables before doing any updates:
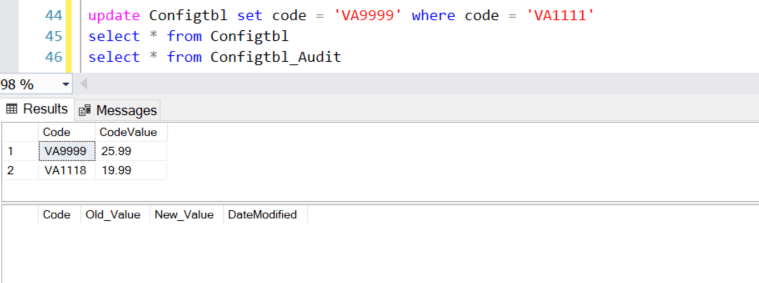
After updating “Code” column in Configtbl table:
After updating “CodeValue” column in Configtbl table:
I’d like to grow my readership. If you enjoyed this blog post, please share it with your friends!