This blog post explains few methods to generate a running number for a SELECT query. Different SQL versions have different ways to achieve this. Let us quickly see ROW_NUMBER() window function with this blog post.
ROW_NUMBER()OVER(PARTITION BY column_list ORDER BY column_list ASC/DESC)
This returns the sequential number for rows. A Quite simple way in SQL Server so far, note that there are different ways we can generate this numbers on group or set depending on sorted manner.Let us see some of those forms in this post. As first step, let us create a
SampleData table populated with few records as below.
Create Table SampleData
(
CourseId Int,
CourseName Varchar(100),
Institute Varchar(100),
Fees Int
)
Insert into SampleData
Values (1,'SQL Server', 'Aptech', 1000),
(1,'SQL Server', 'WowTech', 2000),
(2,'.NET', 'NetTechs', 6000),
(2,'.NET', 'Aptech', 8000),
(2,'.NET', 'SimpleLearn', 7500),
(3,'Python', 'Aptech', 1000),
(3,'Python', 'SimpleLearn', 1500),
(3,'Python', 'PyLearn', 1000),
(3,'Python', 'NetTechs', 1000),
(3,'Python', 'WowTech', 1000)
Select * from SampleData
--Drop Table SampleData
We can create a running number column with row_number window function as below:
Select Row_Number()Over(order by (Select NULL) ASC) Rn,* From SampleData
Select Row_Number()Over(order by (Select NULL) DESC) Rn,* From SampleData
In the above two example, we can see both ASC and DESC returns the same set of ordering and running number because the order by always on NULL value which would have no effect for ASC and DESC.
 Form of generating a running number based on a set of data
Form of generating a running number based on a set of data
Yes, this is based on set or group data. For an example, if we need to generate a running number for a grouped records and so on, you can introduce the Partition by clause to the above query as below.
Select Row_Number()Over( partition by CourseId order by (Select NULL) ASC) Rn,* From SampleData
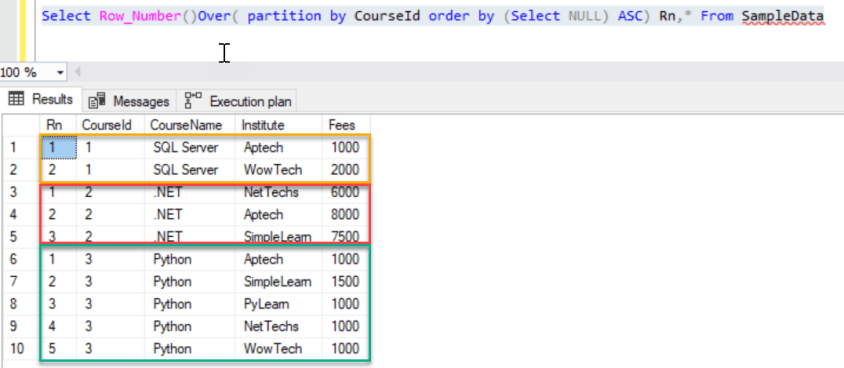 Form of generating a running number based on a set of data with a defined order of data
Form of generating a running number based on a set of data with a defined order of data
In the above example, we have seen the number based on data, now, we are going to quickly see the numbering is based on group of data as well as ordered in a defined way. In our example, we wanted to see the data group for CourseID should be sorted by its Fees in ascending order.
Select Row_Number()Over( partition by CourseId order by Fees ASC) Rn,* From SampleData

Hope this is helpful to understand better of ROW_NUMBER window function in SQL Server.
Hope you enjoyed this post, share your feedback in comment section. Recommending to go through “Microsoft SQL Server – Beginners Guide” series for more information.
I’d like to grow my readership. If you enjoyed this blog post, please share it with your friends!
 Hope this post helps you to understand the difference between RANK() and DENSE_RANK() window functions in SQL Server.
Hope you enjoyed this post, share your feedback in comment section. Recommending to go through “Microsoft SQL Server – Beginners Guide” series for more information.
I’d like to grow my readership. If you enjoyed this blog post, please share it with your friends!
Hope this post helps you to understand the difference between RANK() and DENSE_RANK() window functions in SQL Server.
Hope you enjoyed this post, share your feedback in comment section. Recommending to go through “Microsoft SQL Server – Beginners Guide” series for more information.
I’d like to grow my readership. If you enjoyed this blog post, please share it with your friends!








