In some situations you may face scenarios like “you need to know all the files and folders modified recently or modified after the specific date range to check and remove unnecessary files\folders from the Drive”, for this scenario you can make use of this script.
Pre-requisites:-
- PowerShell
- Access to “xp_cmdshell”
The below is the SQL stored procedure which uses 2 parameters (“Drive\Folder path” and “Date”), Date filter is an optional parameter, if you don’t supply any values, by default it will consider the files\folders which are modified from Yesterday (please note that you can change the default date filter value based on your requirement)
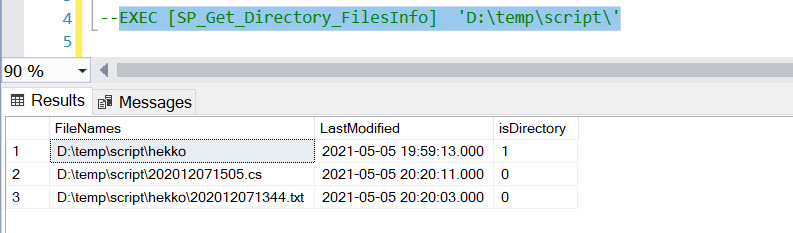
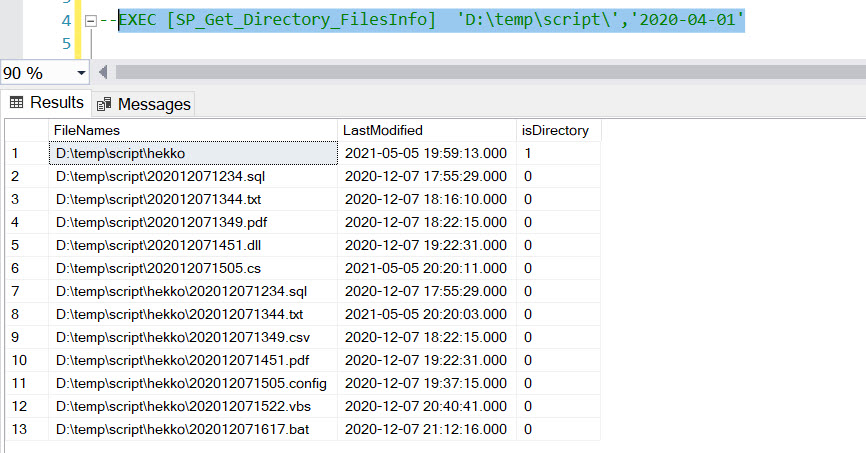
--EXEC [SP_Get_Directory_FilesInfo] 'D:\temp\scripts\','2020-04-01'
--EXEC [SP_Get_Directory_FilesInfo] 'D:\temp\scripts\'
Create or Alter PROCEDURE [dbo].[SP_Get_Directory_FilesInfo]
(@path nvarchar(4000),@yyyymmdd date=NULL) AS
BEGIN
declare @pscript nvarchar(4000)
IF @yyyymmdd IS Null
SET @yyyymmdd= cast(DATEADD(DD,-1,getdate()) as date)
if right(@path,1)='\'
set @path = substring(@path,1,len(@path)-1)
--To avoid using of system drive--
IF (Charindex('C:\',@path)>0 or charindex('c$',@path)>0) BEGIN
Select 'Alert Message!! C-Drive is not supported' Return;
END
--PS Script--
set @pscript ='powershell.exe -ExecutionPolicy Unrestricted -command "Get-ChildItem -Recurse -Path "' + @path +
'" | Where-Object LastWriteTime -ge "' + CAST(@yyyymmdd AS VARCHAR) +
'" | select-Object FullName, @{Name="''LastWriteTime''"; Expression={$_.LastWriteTime.ToString("''yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss''")}}, Mode | Export-CSV -NoTypeInformation -path "' + @path + '\Outputfile.csv"" '
Exec xp_cmdshell @pscript, NO_OUTPUT;
drop table if exists tblcsv_data
create table tblcsv_data (aa nvarchar(max),bb nvarchar(max), mode nvarchar(100))
declare @c nvarchar(4000), @d nvarchar(4000)
set @c = @path + '\Outputfile.csv'
EXEC('
BULK INSERT tblcsv_data
FROM ''' + @c +'''
WITH
(
FIRSTROW = 2,
FIELDTERMINATOR = ''","'', --CSV field delimiter
ROWTERMINATOR = ''\n'', --Use to shift the control to next row
TABLOCK
);
')
set @d = 'del '+ @c
Exec xp_cmdshell @d, NO_OUTPUT;
delete from tblcsv_data where aa like '%Outputfile.csv%'
drop table if exists tbl_FilesInfo
create table tbl_FilesInfo (id bigint identity(1,1),
FileNames nvarchar(max),
LastModified Datetime,
isDirectory bit null
)
insert into tbl_FilesInfo (FileNames,LastModified,isDirectory)
select replace(aa,'"',''),
replace(bb,'"',''),
case when mode='d-----"' then 1 else 0 end isDirectory
from tblcsv_data
if not exists (select 1 from tbl_FilesInfo) Begin
Select 'Please Check!! There are no files having Date Range greater than [' + CAST(@yyyymmdd AS VARCHAR) + ']' as Status
return;
END
select FileNames,
LastModified,
isDirectory
from tbl_FilesInfo
order by isDirectory desc,
LastModified desc
END
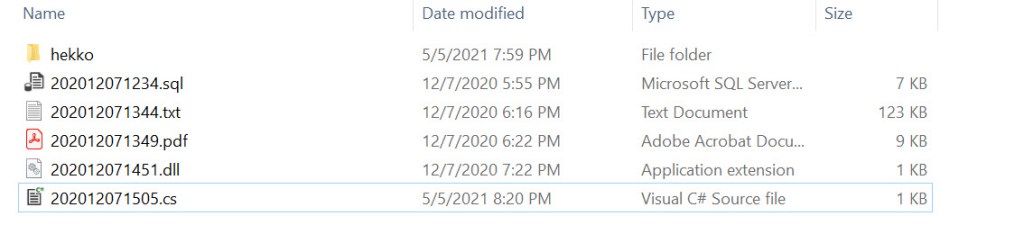
Sample Input Folder:-
Execution of SP with 2 Parameters:-
Execution of SP without Date Parameter:-
In addition to the above, here is the some example of PS scripts which you can directly use it in PowerShell and get the same desired results.
#PS Script 1 output will be displayed in powershell window
Get-ChildItem -Recurse -Path "C:\temp\script" | Where-Object LastWriteTime -ge "2021-04-02" | select-Object FullName, @{Name="''LastWriteTime''"; Expression={$_.LastWriteTime.ToString("''yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss''")}}, @{Name = "Isdirectory"; Expression = {$_.Mode -replace "d-----","1" -replace "-a----","0"}}
#PS Script 2 output will be saved in .csv file
#If you want to save results to text file, please change export file name as Outputfile.txt
Get-ChildItem -Recurse -Path "C:\temp\script" | Where-Object LastWriteTime -ge "2021-04-02" | select-Object FullName, @{Name="''LastWriteTime''"; Expression={$_.LastWriteTime.ToString("''yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss''")}}, @{Name = "Isdirectory"; Expression = {$_.Mode -replace "d-----","1" -replace "-a----","0"}} | Export-CSV "C:\temp\script\Outputfile.csv"
If you enjoyed this blog post, please feel free to share it with your friends!